click on the home button to go to the thocp home page
|
The era of Antiquity (continued) 1810 - 1829 The era of Antiquity can be seen as the era of calculator devices without memory. Dial or indicators serve as output mechanism.
|
pre history | antiquity
| pre industrial era | industrial
era
1620 -
1672 - 1773 - 1810
- 1830 - 1846 - 1874
| Related Articles |
| Related Resources |
|
|

![]() Friedrich Kaufmann constructed an automation that could blow
a trumpet. The mechanism was build from two blowers and 12 "tonal"
tongs. By passing the air over one of the tongs through some sort of an assembly
of levers the air resonated in a particular tone. The horn worked like an amplifier
and gave at the same time the sound of a trumpet. The automation was powered
by a coiled spring. Special to this device was that it was the first of its
kind not using static mechanical parts to do its trick.
Friedrich Kaufmann constructed an automation that could blow
a trumpet. The mechanism was build from two blowers and 12 "tonal"
tongs. By passing the air over one of the tongs through some sort of an assembly
of levers the air resonated in a particular tone. The horn worked like an amplifier
and gave at the same time the sound of a trumpet. The automation was powered
by a coiled spring. Special to this device was that it was the first of its
kind not using static mechanical parts to do its trick.![]()
 December 10, Ada Augusta Byron
is born - later Ada Lovelace. She would be the worlds first programmer by developing
the "MNEMONIC" technique to facilitate assembler commands. In 1980
a programming language will be named after her: ADA. She died on 27 November
1852 in London from a cancer of the uterus.(18)
December 10, Ada Augusta Byron
is born - later Ada Lovelace. She would be the worlds first programmer by developing
the "MNEMONIC" technique to facilitate assembler commands. In 1980
a programming language will be named after her: ADA. She died on 27 November
1852 in London from a cancer of the uterus.(18)
 (13b)
(13b)![]() Charles Xavier
Thomas of Colmar 1785-1870 (France), while serving in the French army, had
the idea of building a calculating machine. His prototype was introduced in
this year. It is the first commercially successful adding machine that was produced
in large quantities.
Charles Xavier
Thomas of Colmar 1785-1870 (France), while serving in the French army, had
the idea of building a calculating machine. His prototype was introduced in
this year. It is the first commercially successful adding machine that was produced
in large quantities.
Thomas used the stepped drum principle of Leibnitz. His invention was the result of 150 years of growing industrialization - eliminating problems that had made the early machines so difficult to perfect. The stepped drum in Thomas' Arithmometer was used in conjunction with a simple system of counting gears and an automatic carry. The success of the machine was due to the many springs and other contrivances that neutralized the momentum of moving parts so they would not carry beyond their intended point - the cause of failure from earlier machines. (13b) But the major innovation was to reverse the operating function in the result registers (up to sixteen digits) that allowed for reliable and stable calculation over extended periods of time without gear realignment.(19)

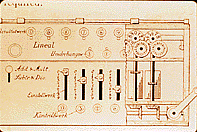
![]() As said the machine was based on the principle developed by
Leibnitz's stepped cylinder (cylinders with sprockets at a predefined position).
The machine was shown to the French Academy of Sciences and became an instant
success.(12) This academy was and still is a
very influential organization that could make or break your idea or machine
by the flick of a pen.
As said the machine was based on the principle developed by
Leibnitz's stepped cylinder (cylinders with sprockets at a predefined position).
The machine was shown to the French Academy of Sciences and became an instant
success.(12) This academy was and still is a
very influential organization that could make or break your idea or machine
by the flick of a pen.
The machine could be set for addition / multiplication or, by moving the lever,
to subtraction / division. It was simple to use and accurate.
For all this, it met with the usual resistance to change. Scientific American
wrote in 1849: "M. Colmar, a French gentleman who invented a calculating
machine about 20 years ago improved it in such a wonderful manner that it is
said to be one of the most astonishing pieces of mechanism that has ever been
invented. But to our view, its complexity shows its delectability."
Which goes to show how wrong predictions could be since types of he Thomas Arithmometer
were still selling into the 20th century. (see also 1823
for an improved version of the calculator)
 |
 |
|
|
Babbage knew three different types of mistakes that could sneak into the making of tables:
By designing a machine that could take over the entire process from calculation
till the production of proto cliches, print-ready, errors would be eliminated. |
![]() Michael Faraday,
known as the father of electricity, reported his discovery of electromagnetic
rotation and build the first of two engines that were driven by electricity.
Michael Faraday,
known as the father of electricity, reported his discovery of electromagnetic
rotation and build the first of two engines that were driven by electricity.
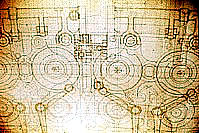
![]() Charles Babbage
designed a calculator. The concept of this machine was that it's operated by
punched cards (see Jacquard 1801) and the results printed on paper. To print
the results was a revolutionary idea. However Babbage thought that the technology
of his days was not sophisticated enough (precision of tooling etc.) to realize
such a machine. But a small scale model is shown at a meeting of the Society.
Charles Babbage
designed a calculator. The concept of this machine was that it's operated by
punched cards (see Jacquard 1801) and the results printed on paper. To print
the results was a revolutionary idea. However Babbage thought that the technology
of his days was not sophisticated enough (precision of tooling etc.) to realize
such a machine. But a small scale model is shown at a meeting of the Society.
 Mechanical (tolerances), financial
(subsidies) and differences of opinion with his chief engineer - Joseph
Clement (a tool engineer and draftsman, a rare combination in these days) -
caused the project to be shelved in 1833. But the concept of the machine is
extremely advanced and probably too far out of most people's league for this
era.
Mechanical (tolerances), financial
(subsidies) and differences of opinion with his chief engineer - Joseph
Clement (a tool engineer and draftsman, a rare combination in these days) -
caused the project to be shelved in 1833. But the concept of the machine is
extremely advanced and probably too far out of most people's league for this
era.

![]() In 1990-1991 Reg Crick en Barry
Holiday(13) - two engineers of the Science
Museum in London - reconstructed the calculating section of the Difference
Engine. They used the original designs. This reconstruction will be called Difference
Engine 2. The engineers at the Science museum in London are still expanding
the machine and in 2002 a printing section was added according to Babbage's
design.
In 1990-1991 Reg Crick en Barry
Holiday(13) - two engineers of the Science
Museum in London - reconstructed the calculating section of the Difference
Engine. They used the original designs. This reconstruction will be called Difference
Engine 2. The engineers at the Science museum in London are still expanding
the machine and in 2002 a printing section was added according to Babbage's
design.
![]() Thomas de Colmar (France) introduced
an improved version of the Arithmometer with all
four basic calculations - add, subtract, divide, and multiply. This device made
no errors.
Thomas de Colmar (France) introduced
an improved version of the Arithmometer with all
four basic calculations - add, subtract, divide, and multiply. This device made
no errors.
![]() The first person to prepare silicon pure enough to allow even
a first-order description of its physical and chemical properties was the Swedish
chemist Jons Jakob Berzelius. His preferred procedure employed metallic potassium
to react with potassium fluorosilicate, a solid white salt, according to the
reaction 4K + K2SiF6 => Si +6KF. The reaction is energetic, the driving force
allowing no give or take, and as a result, the silicon product emerges as finely
divided granules mixed with residual salt.(1) Only in 1941
a physicist named Marcus Olson will succeed to make Silicon pure enough to be
useful in chips
The first person to prepare silicon pure enough to allow even
a first-order description of its physical and chemical properties was the Swedish
chemist Jons Jakob Berzelius. His preferred procedure employed metallic potassium
to react with potassium fluorosilicate, a solid white salt, according to the
reaction 4K + K2SiF6 => Si +6KF. The reaction is energetic, the driving force
allowing no give or take, and as a result, the silicon product emerges as finely
divided granules mixed with residual salt.(1) Only in 1941
a physicist named Marcus Olson will succeed to make Silicon pure enough to be
useful in chips
![]() George Simon Ohm introduces Ohm's law in the book: "Die
galvanische Kette, mathematisch bearbeitet".
George Simon Ohm introduces Ohm's law in the book: "Die
galvanische Kette, mathematisch bearbeitet".
![]() The first electromechanical
clock was constructed in Europe, it only had a bell and no hands. Knowledge
gained from clock mechanism designs shall be important for the coming development
of calculators.
The first electromechanical
clock was constructed in Europe, it only had a bell and no hands. Knowledge
gained from clock mechanism designs shall be important for the coming development
of calculators.
![]() William Austin Burt patents an workable typewriter, the first
writing machine in the USA
William Austin Burt patents an workable typewriter, the first
writing machine in the USA
![]()
|
Last Updated on 14 April, 2004 |
For suggestions please mail the editors |
Footnotes & Reference