click on the home button to go to the home page
|
The Industrial Era 1955 - 1957 The first commercial machines constructed entirely from transistors are put on the market. Fortran is developed. |
pre history | antiquity |
pre industrial era | industrial
era
1947 - 1950 - 1952
- 1955 - 1958
- 1961 - 1963 - 1965
- 1969 - 1970 - 1972
- 1974 - 1976
1978 - 1980 -
1981 - 1982 - 1984 - 1986
- 1989 - 1991 - 1993
- 1994 - 1996 - 2000
- 2002
| Related Articles |
| Related Resources |
|
pre history |
![]() Dartmouth College’s
John McCarthy coins the term "artificial intelligence."
Dartmouth College’s
John McCarthy coins the term "artificial intelligence."
![]() Bell Labs introduces
its first transistor computer. Transistors are faster, smaller and create less
heat than traditional vacuum tubs, making these computers more reliable and
efficient.
Bell Labs introduces
its first transistor computer. Transistors are faster, smaller and create less
heat than traditional vacuum tubs, making these computers more reliable and
efficient.
![]() On 2 October
1955 at 23.45 the power finally shut off, the ENIAC retired. It’s estimated
to have done more arithmetic than the entire human race has done prior to 1945.
Parts of the machine are exibited at the Smithsonian (Washington USA) and a
few other locations in the USA (computerhistory.org).
On 2 October
1955 at 23.45 the power finally shut off, the ENIAC retired. It’s estimated
to have done more arithmetic than the entire human race has done prior to 1945.
Parts of the machine are exibited at the Smithsonian (Washington USA) and a
few other locations in the USA (computerhistory.org).

(7) IBM 702
![]() The first commercial
machine completely constructed from transistors is put on the market by IBM:
series 702
The first commercial
machine completely constructed from transistors is put on the market by IBM:
series 702
The high price of the transistors causeS that the sales are a flop. Still the trend is set by this machine.(1) As you will have noticed there are several "first" fully transistorized computers, but this is the first commercial one.
![]() Allen Newell,
J.C. Shaw and Herbert Simon develop IPL-II, the first artificial intelligence
language.(2)
Allen Newell,
J.C. Shaw and Herbert Simon develop IPL-II, the first artificial intelligence
language.(2)
![]() During
the development of the programming language FORTRAN, Harlan
Herrick introduces the high level language equivalent of a "jump"
instruction in the form of a "GO TO" statement. In 1968
in an article Edsger Dijkstra
will state "GO TO Statement Considered Harmful" thus setting the stage
for more advanced (read: structured) programming.
During
the development of the programming language FORTRAN, Harlan
Herrick introduces the high level language equivalent of a "jump"
instruction in the form of a "GO TO" statement. In 1968
in an article Edsger Dijkstra
will state "GO TO Statement Considered Harmful" thus setting the stage
for more advanced (read: structured) programming.
![]() William Shockley's
Semiconductor Laboratory is the first company established in Silicon Valley,
San Francisco Bay(2)
William Shockley's
Semiconductor Laboratory is the first company established in Silicon Valley,
San Francisco Bay(2)
![]() In March Computer
Usage Company is the first software company to open for business. CUC is founded
by Elmer C Kubie and John W. Sheldon(7)
In March Computer
Usage Company is the first software company to open for business. CUC is founded
by Elmer C Kubie and John W. Sheldon(7)
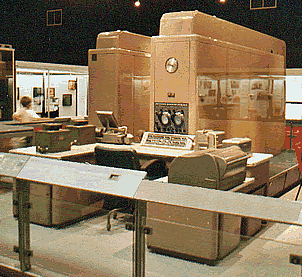
![]() IBM
brings out the "Magnetic Disk Memory" : RAMAC350. Look close at the
picture at the right hand side you will see the cabinet of the RAMAC "harddisk"
IBM
brings out the "Magnetic Disk Memory" : RAMAC350. Look close at the
picture at the right hand side you will see the cabinet of the RAMAC "harddisk"

The era of magnetic disk storage dawned with IBM's shipment of a 305 RAMAC to Zellerbach Paper in San Francisco. The IBM 350 disk served as the storage component for the Random Access Method of Accounting and Control. This "machine" is man's height, contains 50 steel platters coated with a magnetic layer. The platters are mounted on a vertical shaft that drives them around. The read and write heads do not move. The total capacity of the system is 5 million bytes ("characters").(4)(3)

detail of Ramac steel platters
![]() The first Operating System is
designed by Bob Patrick en Owen Mock. The system gets the cryptic name of: GM/NAA-I/O
and is installed on the IBM 704.
The first Operating System is
designed by Bob Patrick en Owen Mock. The system gets the cryptic name of: GM/NAA-I/O
and is installed on the IBM 704.
![]() Researchers at MIT first begin
experimenting with direct keyboard data input.
Researchers at MIT first begin
experimenting with direct keyboard data input.
![]() The
first transistorized computer is completed, three TX-O (Transistorized Experimental
Computer) at the MIT laboratories.(19) Another first is the
TRIDAC to use transistors.
The
first transistorized computer is completed, three TX-O (Transistorized Experimental
Computer) at the MIT laboratories.(19) Another first is the
TRIDAC to use transistors.
Computers based on transistors mark the beginning of the 2-nd Generation of
Computers
![]() APT
(automatic Programmed Tool) is developed by D.T. Ross. With this piece of software
one can create shortcuts in software development. The tool writes the programmers
text or "macro's" out in assembly.
APT
(automatic Programmed Tool) is developed by D.T. Ross. With this piece of software
one can create shortcuts in software development. The tool writes the programmers
text or "macro's" out in assembly.
![]() The case against
IBM of monopolistic practices is settled by forcing IBM to lease and sell its
machines. But IBM ships still 55% of all the data processing equipment.
The case against
IBM of monopolistic practices is settled by forcing IBM to lease and sell its
machines. But IBM ships still 55% of all the data processing equipment.
![]() The first Pegasus, produced by the UK company Ferranti Ltd., went into service
in March 1956, at a time when all of the computers installed in the UK were
designed and built in Britain. Pegasus was noted for its reliability and ease
of use. It was the first computer to have a general register set architecture
– a feature now seen in most modern computers. 40 Pegasus machines were
built by Ferranti Ltd. between 1956 and 1962. Number 25, the only one still
working, was installed in a special gallery in the Science Museum, London(12)
The first Pegasus, produced by the UK company Ferranti Ltd., went into service
in March 1956, at a time when all of the computers installed in the UK were
designed and built in Britain. Pegasus was noted for its reliability and ease
of use. It was the first computer to have a general register set architecture
– a feature now seen in most modern computers. 40 Pegasus machines were
built by Ferranti Ltd. between 1956 and 1962. Number 25, the only one still
working, was installed in a special gallery in the Science Museum, London(12)
![]() A.
Newell, D. Shaw and F. Simon invent IPL (Information Processing language)
A.
Newell, D. Shaw and F. Simon invent IPL (Information Processing language)

![]() The
acronym AI - artificial
intelligence - is coined by John McCarty
The
acronym AI - artificial
intelligence - is coined by John McCarty
![]() Siemens (Germany) starts to produce
the 2002 computer in series. It is one of the fully transistorized computers
in Europe.
Siemens (Germany) starts to produce
the 2002 computer in series. It is one of the fully transistorized computers
in Europe.

![]() Digital
Equipment Corporation (DEC) is founded by Ken Olsen and Harlan Anderson. Starting
out with laboratory and scientific modules. Their first computer the PDP 1 (Programmed
Data Processor) will be released in 1960 and will get many successful descendants.
DEC will be one of the most important computer producers of the world.
Digital
Equipment Corporation (DEC) is founded by Ken Olsen and Harlan Anderson. Starting
out with laboratory and scientific modules. Their first computer the PDP 1 (Programmed
Data Processor) will be released in 1960 and will get many successful descendants.
DEC will be one of the most important computer producers of the world.
![]() G.W.A. Dummer, exhibits during
the Royal Radar Exhibition in England a model of an Integrated circuit.
G.W.A. Dummer, exhibits during
the Royal Radar Exhibition in England a model of an Integrated circuit.
![]() Jack
Kilby and Robert Noyce invent
the SILICON WAFER. With this they lay the foundation of the: Third Generation
of Computers.
Jack
Kilby and Robert Noyce invent
the SILICON WAFER. With this they lay the foundation of the: Third Generation
of Computers.
![]() John
Bardeen, John Schrieffer and Leon Cooper (USA) develop a theoretical model
for Super Conductivity. We shall see later that super conductivity becomes
more important when the critical limits of chip design comes near. Critical
means how many transistors or other elements can be integrated on one single
chip without creating interference. In Dr. John Bardeen wins a Nobel Prize for
work in Superconductivity
John
Bardeen, John Schrieffer and Leon Cooper (USA) develop a theoretical model
for Super Conductivity. We shall see later that super conductivity becomes
more important when the critical limits of chip design comes near. Critical
means how many transistors or other elements can be integrated on one single
chip without creating interference. In Dr. John Bardeen wins a Nobel Prize for
work in Superconductivity
![]() FORTRAN-1
is formally published. This first of all kind of high level languages is developed
by John Backus and his team for IBM. FORTRAN uses notation that have a strong
resemblance with those used in algebraic notation. For that Fortran will become
very popular with scientists and technicians.
FORTRAN-1
is formally published. This first of all kind of high level languages is developed
by John Backus and his team for IBM. FORTRAN uses notation that have a strong
resemblance with those used in algebraic notation. For that Fortran will become
very popular with scientists and technicians.

![]() Control
Data Corporation is founded by William C. Morris and a group of engineers (amongst
whom Seymour Cray) from Sperry
Rand
Control
Data Corporation is founded by William C. Morris and a group of engineers (amongst
whom Seymour Cray) from Sperry
Rand
![]() The
first issue of Datamation is released.
The
first issue of Datamation is released.
![]() Nippon Telegraph
and Telephone Corp (Japan). develops the Musasino-1, the
first parametron computer. It uses 519 vacuum tubes and 5,400 parametrons—logic
elements based on the principle of parametric excitation and invented by Eiji
Goto in 1954.
Nippon Telegraph
and Telephone Corp (Japan). develops the Musasino-1, the
first parametron computer. It uses 519 vacuum tubes and 5,400 parametrons—logic
elements based on the principle of parametric excitation and invented by Eiji
Goto in 1954.
![]() A first attempt
to immitatie human intelligence in a simulacron is attempted by Herbert. A.
Simon, Allen Newell & J.C. Shaw. They devise a logic theory machine (first
proof by machine) the General Problem Solver (GPS). The method for testing the
theory involves developing a computer simulation and then comparing the results
of the simulation with human behavior in a given task.
A first attempt
to immitatie human intelligence in a simulacron is attempted by Herbert. A.
Simon, Allen Newell & J.C. Shaw. They devise a logic theory machine (first
proof by machine) the General Problem Solver (GPS). The method for testing the
theory involves developing a computer simulation and then comparing the results
of the simulation with human behavior in a given task.
![]() on
aritficial Intelligence
and man-machine simulations
on
aritficial Intelligence
and man-machine simulations
![]()
| Last Updated on October 5, 2004 | For suggestions please mail the editors |
Footnotes & References
| 1 | IBM 1984; Van glazenhuis naar bijna elke werkplek ; eng: from glasshouse to every one'swork place |
| 2 | Marian Bozdoc, Auckland NZ, www.bozdoc.f2s.com |
| 3 | TCM |
| 4 | One is exhibited in the Boston Computer Museum (USA) |
| 5 | http://cswww.essex.ac.uk/Pegasus/ |
| 6 | photo the history of computing foundation |
| 7 | Annals of History of computing (IEEE) 1994 vol 16 no2 pg 65 |
| 8 | http://www.recherche.enac.fr/~alliot/COURS/sld098.htm |
| 13 | Picture THOCF |