click on the home button to go to the home page
|
The Industrial Era 1986-1990 The Fourth generation of computers starts approximately in this era. These computers are characterized by fully electronic and programmable models. ICs are built which contain more than 500.000 components. With this step the FOURTH GENERATION of computers started
|
pre history | antiquity |
pre industrial era | industrial
era
1947
- 1950 - 1952 - 1955
- 1958 - 1961 - 1963
- 1965 - 1969 - 1970
- 1972 - 1974 - 1976
- 1978 - 1980 -
1981 - 1982 - 1984 - 1986
- 1989 - 1991 - 1993
- 1994 - 1996 - 2000
- 2002
| Related Articles |
| History of Software |
| Related Resources |
|
pre history |
![]() Integrated
software (Word processor, Spreadsheet, Database, Graphics, Communication) are
now common amongst advanced users. The strict line between professional and
nonprofessional users is more and more disappearing. The only limitation
is the price of new software and hardware. Businesses can afford more expensive
hard and software than the nonprofessional. The latter started with computers
soon called micro computers or home computers. The most famous are the Commodore
64 and Apple II. Also other small micro computers became affordable. They were
priced from 300 US$ and up, e.g. Timex Sinclair SX 80
Integrated
software (Word processor, Spreadsheet, Database, Graphics, Communication) are
now common amongst advanced users. The strict line between professional and
nonprofessional users is more and more disappearing. The only limitation
is the price of new software and hardware. Businesses can afford more expensive
hard and software than the nonprofessional. The latter started with computers
soon called micro computers or home computers. The most famous are the Commodore
64 and Apple II. Also other small micro computers became affordable. They were
priced from 300 US$ and up, e.g. Timex Sinclair SX 80
![]() Prodigy founded by Sears and
IBM
Prodigy founded by Sears and
IBM
Sears and IBM plan to launch a national online service, dubbed Prodigy in 1987.
Prodigy becomes one of the three leading online services before it loses ground
to the World Wide Web in the mid-1990s. The company is bought out by its management
in 1996 and becomes an Internet service provider. (6)
![]() The first RISC
computer of IBM, the RT PC, is introduced on the market. The idea of Reduced
Instruction Set Computers originated in 1976. This new way to construct a processor
makes that it can only handle single instructions, which only last one clock
cycle. Because of the one cycle process, it seems that the CPU program runs
faster than the original full instruction set CPU.
The first RISC
computer of IBM, the RT PC, is introduced on the market. The idea of Reduced
Instruction Set Computers originated in 1976. This new way to construct a processor
makes that it can only handle single instructions, which only last one clock
cycle. Because of the one cycle process, it seems that the CPU program runs
faster than the original full instruction set CPU.

![]() The
first IBM portable computer (IBM 5140)
"The Convertible" becomes a huge flop. It is too expensive, has not
enough memory and most people find the machine too heavy.
The
first IBM portable computer (IBM 5140)
"The Convertible" becomes a huge flop. It is too expensive, has not
enough memory and most people find the machine too heavy.
![]() Of course,
Hewlett Packard can not remain behind and introduces a complete new line of
computers based on the HP Precision Architecture (1).
The project received the code name "Spectrum" and the costs of development
over 5 years are more than 250 million dollars. It is HP's most expensive research
project up to a long time to come.
Of course,
Hewlett Packard can not remain behind and introduces a complete new line of
computers based on the HP Precision Architecture (1).
The project received the code name "Spectrum" and the costs of development
over 5 years are more than 250 million dollars. It is HP's most expensive research
project up to a long time to come.
![]() The first TRANSPUTER,
a computer on a chip, is developed in Japan.
The first TRANSPUTER,
a computer on a chip, is developed in Japan.
![]() The commercial
introduction of the MINI-SUPER (computer) with a relatively low price of 2 million
US dollars has the same computational power as the first generation super computers
with regard to the speed of computing.
The commercial
introduction of the MINI-SUPER (computer) with a relatively low price of 2 million
US dollars has the same computational power as the first generation super computers
with regard to the speed of computing.
![]() The CD ROM
(compact disc read only memory) is introduced by SONY. On this disc one can
store 650MB of information.
The CD ROM
(compact disc read only memory) is introduced by SONY. On this disc one can
store 650MB of information.
![]() IBM introduced
the 1 Mbit (128 Kb) memory chip. At the same time a 1Mb chip is introduced in
Japan.
IBM introduced
the 1 Mbit (128 Kb) memory chip. At the same time a 1Mb chip is introduced in
Japan.
![]() SAA (Systems
Applications Architecture) will form the bridge between all IBM systems, such
as the systems S/370, S/3X and PS/2 models can communicate through this software.
SAA (Systems
Applications Architecture) will form the bridge between all IBM systems, such
as the systems S/370, S/3X and PS/2 models can communicate through this software.
SAA is a development philosophy which is first launched by IBM. If implemented
thoroughly it takes care that the systems as well as the software have the same
look and would be compatible with other soft- and hardware. This means that
the buildup of the information screens are bounded to rules which increases
the efficiency and ergonomy of the information systems.
![]()
 Philip
K. Katz develops PKArc. A program that makes files smaller, hence: compression.
After a legal dispute several years later the program will be renamed into PKZip.
The advantage of using a compression program is that compressed files will take
a shorter time to send or receive from other computers, but they also take less
space on your hard disk.
Philip
K. Katz develops PKArc. A program that makes files smaller, hence: compression.
After a legal dispute several years later the program will be renamed into PKZip.
The advantage of using a compression program is that compressed files will take
a shorter time to send or receive from other computers, but they also take less
space on your hard disk.
Katz puts the program into the shareware domain: pay only as you like and use
it. He soon will make a fortune and that was something totally not anticipated
by him, as he later will tell a journalist of the Milwaukee Journal.(5)
![]() In this year
the stock market on Wallstreet is fully automated. It only took the traders
a couple of days to realize that they could trade from their desks using
their own computers as well. Within one week the system went in operation the
trading rooms will be empty. The stock market's management was quite surprised,
which is an under statement of their feelings. Also they feel a little
embarrassed with the speed Wallstreet turned into an electronic ghost
town.
In this year
the stock market on Wallstreet is fully automated. It only took the traders
a couple of days to realize that they could trade from their desks using
their own computers as well. Within one week the system went in operation the
trading rooms will be empty. The stock market's management was quite surprised,
which is an under statement of their feelings. Also they feel a little
embarrassed with the speed Wallstreet turned into an electronic ghost
town.
![]() Berkeley Softworks
introduces the Operatingsystem GEOS, initially thought for the Commodore 64
and later ported to other computers (CPU's) as well. This was a sleek and fast
OS that had less bloath than MS window's.(8)
Berkeley Softworks
introduces the Operatingsystem GEOS, initially thought for the Commodore 64
and later ported to other computers (CPU's) as well. This was a sleek and fast
OS that had less bloath than MS window's.(8)
![]() On April 2, IBM officially introduces
a new family of personal computers: the PS/2-series. Starting with the 30
series (8086 CPU) and ending with series 80, based on the 80386 CPU. This system-line
introduced the so-called VGA graphics (Video Graphics Array), a new data concept:
Micro Channel Architecture (MCA). The 3 1/2" floppy disk drives which
are mounted in the type 68000 machines (Apple, Amiga) are now installed in the
IBM PS/2 as well.
On April 2, IBM officially introduces
a new family of personal computers: the PS/2-series. Starting with the 30
series (8086 CPU) and ending with series 80, based on the 80386 CPU. This system-line
introduced the so-called VGA graphics (Video Graphics Array), a new data concept:
Micro Channel Architecture (MCA). The 3 1/2" floppy disk drives which
are mounted in the type 68000 machines (Apple, Amiga) are now installed in the
IBM PS/2 as well.
But there is not an operating system (OS/2) available at the introduction of
the new IBM PS/2 machines. Quickly hybrids of these OS's are getting to
the market and fill in the gap left by IBM, such as: Pcmos 386, Windows/286,
Windows/386 and similar ones.
![]() When OS/2 finally
appears on the market it is big, slow and riddled with bugs. However the
release of OS/2 allowed a mouse to be used with IBM PCs for the first time.
When OS/2 finally
appears on the market it is big, slow and riddled with bugs. However the
release of OS/2 allowed a mouse to be used with IBM PCs for the first time.
![]() In addition,
in April MS-DOS 3.3 appears on the market. This version can create partitions
on the hard disc. DOS 3.3 appears to be one of the most stable versions for
DOS operating systems for the next four years.
In addition,
in April MS-DOS 3.3 appears on the market. This version can create partitions
on the hard disc. DOS 3.3 appears to be one of the most stable versions for
DOS operating systems for the next four years.
![]() IBM starts
with the development of the GF-11. This should be a computer with 576 parallel
processors each with 2Mb memory and every chip should be able to execute 20
million computations per second. In this way the GF-11 could make, at top speed,
11 billion computations per second.
IBM starts
with the development of the GF-11. This should be a computer with 576 parallel
processors each with 2Mb memory and every chip should be able to execute 20
million computations per second. In this way the GF-11 could make, at top speed,
11 billion computations per second.
![]() Inmos introduces
the T800 transputer (2 Mega Flops) that slashes all records for its speed.
Inmos introduces
the T800 transputer (2 Mega Flops) that slashes all records for its speed.
Inmos also introduces the first transputer with a numerical coprocessor. With
this transputer possibilities seem unlimited for scientific computations.
![]() The 1.44 Mb
micro floppy drive and its accompanying floppy discs are introduced.
The 1.44 Mb
micro floppy drive and its accompanying floppy discs are introduced.
![]() Bill Atkinson
develops with his team (around twenty people amongst which is Dan Winkler (
programmer ) and Marge Boots ( illustrator) the HyperCard system. It is
one of the predecessors of Hypertext but based on programming languages such
as SmallTalk and Logo. HyperCard is an author system and meant to form links
for a vast amount of unstructured information. The links are called: "hyper
links".
Bill Atkinson
develops with his team (around twenty people amongst which is Dan Winkler (
programmer ) and Marge Boots ( illustrator) the HyperCard system. It is
one of the predecessors of Hypertext but based on programming languages such
as SmallTalk and Logo. HyperCard is an author system and meant to form links
for a vast amount of unstructured information. The links are called: "hyper
links".
For the time being this system will only run on the Apple Macintosh. It will
take several years before other platforms (amongst them Intel) make a similar
Hyper Card system available.
![]() Eli
Yablonovitch of Bellcore corporation describes the theory of how to store
light pulses into memory blocks. The memory blocks consists of photonic crystals
that contains "chambers" in where the light beams are trapped. This
can be done by making the chamber the exact size of the wavelength of the light
and the diffraction of the material used is large enough to create a reflection
between the "wall" of the chamber and the medium in which the light
is trapped.(3)
Eli
Yablonovitch of Bellcore corporation describes the theory of how to store
light pulses into memory blocks. The memory blocks consists of photonic crystals
that contains "chambers" in where the light beams are trapped. This
can be done by making the chamber the exact size of the wavelength of the light
and the diffraction of the material used is large enough to create a reflection
between the "wall" of the chamber and the medium in which the light
is trapped.(3)
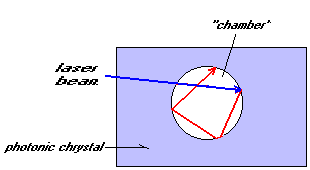
It will take about 10 years to come to a next step in this technology by two
Dutch scientists. (1998)
Light will become the future power to drive computers. It is faster and uses less energy. But this technology is much more complicated than that of electrons. And the needed theories are still not known, a lot of work needs to be done. Science is not yet advanced enough to make any practical and marketable device.
![]() The RISC architecture
is invented by a research team on Berkely university under projectleader David
A. Patterson. This research will result in the SPARC processor going to be used
by Sun Microsystems and Fujitsu.
The RISC architecture
is invented by a research team on Berkely university under projectleader David
A. Patterson. This research will result in the SPARC processor going to be used
by Sun Microsystems and Fujitsu.
At Stanford a team led by John Hennesy, also invented the concept of RISC (Reduced
Instruction Set Computers).
The microprocessors which emerged from these 2 projects the MIPS and SPARC are
used in most modern workstations.
![]() The
OS/2 developers version 1.1 is on the market. The OS/2 operating system
still does not make use of all the possibilities of the so-called Protected
Mode.
The
OS/2 developers version 1.1 is on the market. The OS/2 operating system
still does not make use of all the possibilities of the so-called Protected
Mode.
![]() Finally, IBM
entered the super computer arena, and start with a research group with some
of the ex-employees from CRAY.
Finally, IBM
entered the super computer arena, and start with a research group with some
of the ex-employees from CRAY.
![]() The NeXT (68030
CPU) computer is being introduced after two years of research and developed
by Steve Jobs (one of the developers and inventors of the APPLE computer).
For the time being the computer is only sold to students for the high price
of US$ 10.000. The limited software available is written in the language C and
offers a development environment under UNIX.
The NeXT (68030
CPU) computer is being introduced after two years of research and developed
by Steve Jobs (one of the developers and inventors of the APPLE computer).
For the time being the computer is only sold to students for the high price
of US$ 10.000. The limited software available is written in the language C and
offers a development environment under UNIX.
![]() Maxis releases
Sim City, a video game that simulates the building and maintaining a of a city.
The city has to be build up from scratch by placing houses, factories, powerplants,
police and fire stations on the "playing" board". The population
of the city grows accordingly and thus the tax income of the city. The aim is
to make as much money as possible while keeping your citizens happy. Low taxes
good public transportation security are factors that keeps them happy. To keep
the game appealing to players accidents, crime, fires and disasters were factors
of disaster randomly introduced
Maxis releases
Sim City, a video game that simulates the building and maintaining a of a city.
The city has to be build up from scratch by placing houses, factories, powerplants,
police and fire stations on the "playing" board". The population
of the city grows accordingly and thus the tax income of the city. The aim is
to make as much money as possible while keeping your citizens happy. Low taxes
good public transportation security are factors that keeps them happy. To keep
the game appealing to players accidents, crime, fires and disasters were factors
of disaster randomly introduced
The term SIM will become a word for anything that is simulated by computers
and stands for many other simulation games.
![]() Introduction
of MS-DOS 4.0 which is succeeded rapidly by version 4.01. This version
is only available via OEM[(2)] sales.
DOS 4.XX can manage partitions larger then 32Mb, and can work with expanded
memory. Has a DOS shell that looks like a Windows GUI, also mouse support and
PCTools and Norton Utilities like programs are remastered from the originals.
In short, it has a similar look like MS-Windows, but MS-Windows is an
overlay-operating-system, while MS-DOS works like a shell. This version is riddled
with bugs like a Swiss cheese and will never become a success.
Introduction
of MS-DOS 4.0 which is succeeded rapidly by version 4.01. This version
is only available via OEM[(2)] sales.
DOS 4.XX can manage partitions larger then 32Mb, and can work with expanded
memory. Has a DOS shell that looks like a Windows GUI, also mouse support and
PCTools and Norton Utilities like programs are remastered from the originals.
In short, it has a similar look like MS-Windows, but MS-Windows is an
overlay-operating-system, while MS-DOS works like a shell. This version is riddled
with bugs like a Swiss cheese and will never become a success.
![]() Nine leading
PC producers present a new concept, the Enhanced Industry Standard Architecture
(EISA). It will provide an alternative for the Micro Channel Architecture 32
bits bus concept introduced by IBM. This action is mainly a response against
the licensing policy of IBM that does not want to release the MCA concept for
use. Later only against an abnormal high price.
Nine leading
PC producers present a new concept, the Enhanced Industry Standard Architecture
(EISA). It will provide an alternative for the Micro Channel Architecture 32
bits bus concept introduced by IBM. This action is mainly a response against
the licensing policy of IBM that does not want to release the MCA concept for
use. Later only against an abnormal high price.
![]() INTEL offers
the 80386SX processor, a cheaper version of the 80386. It has a 6 bit data bus
and a 24 bits address bus (just like the 80286) [DOS 12/1988, p86]
INTEL offers
the 80386SX processor, a cheaper version of the 80386. It has a 6 bit data bus
and a 24 bits address bus (just like the 80286) [DOS 12/1988, p86]
![]() Internet Assigned
Numbers Authority established
Internet Assigned
Numbers Authority established
The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority is established by the government. Based
in Marina del Rey, California, and headed by influential Internet pioneer Jonathan
Postel, the group will manage the registration of domain names for the next
decade.(6)
![]() Internet Relay
Chat invented
Internet Relay
Chat invented
Finnish student Jarkko Oikarinen develops Internet Relay Chat, which will grow
into a major Internet application, attracting millions of people to communicate
in real time. Notably, Internet Relay Chat will be used to send real-time information
during the Gulf War and other crises during the 1990s.(6)
![]() Worm plagues
Internet
Worm plagues
Internet
A malicious program called a worm affects some six thousand computers, ARPA
forms the Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT). (6)
![]()
| Last Updated on February 5, 2004 | For suggestions please mail the editor in chief |
Footnotes & References