click on the home button to go to the home page
|
The Industrial Era 1978 - 1979 The Third Generation of computers really gets off now,
IBM is entering the micro computermarket. Less and less manufacturers
keep their systems closed to other suppliers. |
pre history | antiquity |
pre industrial era | industrial
era
1947
- 1950 - 1952 - 1955
- 1958 - 1961 - 1963
- 1965 - 1969 - 1970
- 1972 - 1974 - 1976
- 1978 - 1980 -
1981 - 1982 - 1984 - 1986
- 1989 - 1991 - 1993
- 1994 - 1996 - 2000
- 2002
| Related Articles |
| Related Resources |
|
pre history |
![]() The Xerox Corporation
created a TCP enhancement: Internet Protocol (IP), a separate program that handles
the routing of individual messages.
The Xerox Corporation
created a TCP enhancement: Internet Protocol (IP), a separate program that handles
the routing of individual messages.
Combined with the TCP protocol from 1979, the two became known as TCP/IP and
represented the standard system used in most large networks.
![]() INTEL introduced
the 16-bit-8086 chip and the coprocessor 8087. These chips were causing much
excitement. But were not quickly accepted mainly because they were too advanced.(33) In later years though other chips, with
a higher magnitude of possibilities, would dominate the market for years to
come. It used 16 bit registers, a 16 bit databus, and 28.000 transistors using
3 micron technology. It can access 1 MB of memory. Speed is 0.33 MIPS. Later
speeds included 8 and 10 MHz, 0.66 and 0.75 MIPS.
INTEL introduced
the 16-bit-8086 chip and the coprocessor 8087. These chips were causing much
excitement. But were not quickly accepted mainly because they were too advanced.(33) In later years though other chips, with
a higher magnitude of possibilities, would dominate the market for years to
come. It used 16 bit registers, a 16 bit databus, and 28.000 transistors using
3 micron technology. It can access 1 MB of memory. Speed is 0.33 MIPS. Later
speeds included 8 and 10 MHz, 0.66 and 0.75 MIPS.
![]() PC's grew into
complete systems: keyboard, display, floppy drives, memory, BIOS etc. and memory
was expanded up to 16 Kb.
PC's grew into
complete systems: keyboard, display, floppy drives, memory, BIOS etc. and memory
was expanded up to 16 Kb.
![]() The first 64
Kb (8 Kb) RAM memory chip were being produced in mass by IBM.
The first 64
Kb (8 Kb) RAM memory chip were being produced in mass by IBM.
![]() A new breed
of programs is introduced: the OPERATING
SYSTEM (OS)
A new breed
of programs is introduced: the OPERATING
SYSTEM (OS)
 The Datamaster system/23
was designed by IBM engineers. David J. Bradley wrote the operating system for
it. System 23 had two 8 inch Floppy's, a video screen, and a keyboard integrated
into one single case.
The Datamaster system/23
was designed by IBM engineers. David J. Bradley wrote the operating system for
it. System 23 had two 8 inch Floppy's, a video screen, and a keyboard integrated
into one single case.
The experience gained with this project proved to be of great importance at the development of the PC in 1980.
Another one of the first micro computer developments in this field was CP/M (1973); Control Program for Micro computers and developed by Gary Kildall of Digital Research.
An operating System lightens the burdens of a programmer to rewrite a program
every time it is going to be used on a different machine, within the limits
of a compatible CPU off course.
This so called OS was because of its compactness attractive enough to be accepted
by all other manufacturers as a de facto standard.
Now the software industry really could take off and make affordable programs,
meaning the price of software could come down. Software was still expensive
and only businesses could afford to buy software packages like WordStar and
VisiCalc
One question remains: will the hardware industry also start to standardize.
![]() Computer Headware
announces WHATSIT the first database manager.
Computer Headware
announces WHATSIT the first database manager.
![]() Micro Pro Int.
announced Word Master a word processor precursor to Word Star
Micro Pro Int.
announced Word Master a word processor precursor to Word Star

![]() Dan
Bricklin and Bob Frankston (USA)
developed the first commercial spreadsheet: 'VisiCalc'. The first "useful"
(read business type) program for Personal Computers. Of which the next year
900.000 copies will be sold and distributed by Software Ants. Initially available
only for Apple II, the program was an instant success.
Dan
Bricklin and Bob Frankston (USA)
developed the first commercial spreadsheet: 'VisiCalc'. The first "useful"
(read business type) program for Personal Computers. Of which the next year
900.000 copies will be sold and distributed by Software Ants. Initially available
only for Apple II, the program was an instant success.
![]() The
first BBS (Bulletin
Board System) created by Ward Christen (USA), member of a Chicago went "on
air" this year. He wrote the BBS program for a do it your self computer
(a Northstar Horizon CP/M-machine) that could answer a 110-bps-modem.
The
first BBS (Bulletin
Board System) created by Ward Christen (USA), member of a Chicago went "on
air" this year. He wrote the BBS program for a do it your self computer
(a Northstar Horizon CP/M-machine) that could answer a 110-bps-modem.
Members (often a computerclub) could dial up a BBS to leave a message or download
software(34). In the future the functionality
of a BBS shall not expand much beyond the basics: download directories, interest
groups, and electronic mail (e-mail).
![]() There was a
lot of resistance in the United Kingdom against the overpriced American computers
for private use. Responding on this signal in the market a company called Lynx
(subsidiary of NASCO USA) introduced an affordable "computer kit".
Instead of using a monitor people had to use their own television. For data
storage a cassette recorder was used. The operating system was embedded in an
8Kbyte EPROM(35). The kit consisted
of a: Mostek Z80 processor, QWERTY keyboard, 16Kbyte of memory and was sold
for 250 Sterling Pound. (App. 750 U$)
There was a
lot of resistance in the United Kingdom against the overpriced American computers
for private use. Responding on this signal in the market a company called Lynx
(subsidiary of NASCO USA) introduced an affordable "computer kit".
Instead of using a monitor people had to use their own television. For data
storage a cassette recorder was used. The operating system was embedded in an
8Kbyte EPROM(35). The kit consisted
of a: Mostek Z80 processor, QWERTY keyboard, 16Kbyte of memory and was sold
for 250 Sterling Pound. (App. 750 U$)
![]() Oracle's first
version of the Oracle database management system (DBMS) was released and became
the standard database for mainframe
and Client/Server networking.(25)
Oracle's first
version of the Oracle database management system (DBMS) was released and became
the standard database for mainframe
and Client/Server networking.(25)
![]() Niklaus Wirth
developed Modula -2 derived from Pascal with a few improvements. It was implemented
one year later on the PDP-11 using the Medos -2 operating system.(25)
Niklaus Wirth
developed Modula -2 derived from Pascal with a few improvements. It was implemented
one year later on the PDP-11 using the Medos -2 operating system.(25)

![]() Texas Instruments
introduced a computer for kids, the Speak & Spell talking learning aid,
for ages 7 and up. In fact a revolutionary idea to have the kids type in the
words and the machine spoke it aloud. It meant the perfect learning aid, taking
into account the state of the art speech synthesis at that time.
Texas Instruments
introduced a computer for kids, the Speak & Spell talking learning aid,
for ages 7 and up. In fact a revolutionary idea to have the kids type in the
words and the machine spoke it aloud. It meant the perfect learning aid, taking
into account the state of the art speech synthesis at that time.
![]() Epson announced
the MX-80 dot matrix printer, which established
a new standard in high performance printing for a low price. The machine is
created by Chris Rutkowski and will be put
on the market in 1980. Chris still has one of the very first machines: serial
nr. 0000002 and it sits in a box in his garage. According to Chris number #1
never came to America (38)
Epson announced
the MX-80 dot matrix printer, which established
a new standard in high performance printing for a low price. The machine is
created by Chris Rutkowski and will be put
on the market in 1980. Chris still has one of the very first machines: serial
nr. 0000002 and it sits in a box in his garage. According to Chris number #1
never came to America (38)

![]() Atari announced
the Atari 400 and 800 personal computers both with a 6502 CPU
Atari announced
the Atari 400 and 800 personal computers both with a 6502 CPU
![]() Houston Inst.
announced the Hi Plot plotter.
Houston Inst.
announced the Hi Plot plotter.
![]() Summagraphics
announced Bit Pad the first digitizer.
Summagraphics
announced Bit Pad the first digitizer.
![]() The first "hypermedia"
presentation, the Aspen Movie Map, is created by MIT researchers.(3)
The first "hypermedia"
presentation, the Aspen Movie Map, is created by MIT researchers.(3)
![]() Microsoft
developed a database an electronic file system
Microsoft
developed a database an electronic file system
![]() Texas Instruments
introduced the TI 99/4 (not the 4A) for an initial price of US$ 1500. It used
the TI 9940 16 bits processor. This is another example of a high tech innovation
that was too expensive to become a success. But TI refuses to bring down the
price instead started to develop the 99/4A a cheaper model.
Texas Instruments
introduced the TI 99/4 (not the 4A) for an initial price of US$ 1500. It used
the TI 9940 16 bits processor. This is another example of a high tech innovation
that was too expensive to become a success. But TI refuses to bring down the
price instead started to develop the 99/4A a cheaper model.
![]() Motorola introduced
the powerful 16bit 6800 chip which operated internally with 32bit registers.
This processor was used in graphical orientated computers.
Motorola introduced
the powerful 16bit 6800 chip which operated internally with 32bit registers.
This processor was used in graphical orientated computers.
![]() Intel introduced
the 8088 which uses a 32bit data bus, but inside still operated on a 16 bit
architecture. The development made the acceptance of the 8086/8087 more easier
because they could be used on the much cheaper 8bit versions. This chip formed
the basis of the IBM PC.
Intel introduced
the 8088 which uses a 32bit data bus, but inside still operated on a 16 bit
architecture. The development made the acceptance of the 8086/8087 more easier
because they could be used on the much cheaper 8bit versions. This chip formed
the basis of the IBM PC.

![]() Sinclair
Research introduced the ZX80 on the market. The machine had 1 Kb of memory,
3.25 MHz clock speed, weighed under 300 grams and sold at for those day very
low price. The system made use of music cassettes to store data and memory could
be expanded up to 16Kbyte. Equipped with an on board BASIC the computer could
be directly plugged into your television. Also the keyboard was made from foil
contacts with a slightly rugged surface. By pressing the foil which covered
the entire "keyboard" surface a contact was closed that was surface
mounted right on the PCB. No mechanical parts were needed at all. (1)
Sinclair
Research introduced the ZX80 on the market. The machine had 1 Kb of memory,
3.25 MHz clock speed, weighed under 300 grams and sold at for those day very
low price. The system made use of music cassettes to store data and memory could
be expanded up to 16Kbyte. Equipped with an on board BASIC the computer could
be directly plugged into your television. Also the keyboard was made from foil
contacts with a slightly rugged surface. By pressing the foil which covered
the entire "keyboard" surface a contact was closed that was surface
mounted right on the PCB. No mechanical parts were needed at all. (1)
The machine could not display images while it was calculating or storing / loading
data the screen blanked out during that process.
![]() In this year two famous games
were introduced: Space Invaders and Pacman. In the game Space Invaders the earth
was under attack by aliens and you had to safe the planet. At first this game
was only introduced in amusement arcades but later on it also was available
at all kinds of computers even programmers made this game available on mainframes.
In the game Pacman you have to eat as many dots as possible before you got caught
by ghosts. Both games would last for decades in different versions.
In this year two famous games
were introduced: Space Invaders and Pacman. In the game Space Invaders the earth
was under attack by aliens and you had to safe the planet. At first this game
was only introduced in amusement arcades but later on it also was available
at all kinds of computers even programmers made this game available on mainframes.
In the game Pacman you have to eat as many dots as possible before you got caught
by ghosts. Both games would last for decades in different versions.
![]() MicroPro, founded
by Rob Barnaby and Seymon Rubenstein, developed the program WordStar which will
become the most widely spread word processor in this decade. It is written by
Rob Barnaby and made available for Intel 8088, Z-80 base CP/M systems ( ported
by Seymour Rubenstein)
MicroPro, founded
by Rob Barnaby and Seymon Rubenstein, developed the program WordStar which will
become the most widely spread word processor in this decade. It is written by
Rob Barnaby and made available for Intel 8088, Z-80 base CP/M systems ( ported
by Seymour Rubenstein)
![]() Personal
Software released VisiCalc for the Apple II and sold it for U$100. This combination
pushed the sales of the Apple II sky high. A perfect combination and though
the Apple II was expensive, the software made it worthwhile.
Personal
Software released VisiCalc for the Apple II and sold it for U$100. This combination
pushed the sales of the Apple II sky high. A perfect combination and though
the Apple II was expensive, the software made it worthwhile.

In May Sofware Arts demonstrated VisiCalc at the 4th Westcoast Computer Fair. The VisiCalc program was written by Dan Bricklin and Bob Frankston during 1978-1979 under the company name Software Arts, under contract to Personal Software.
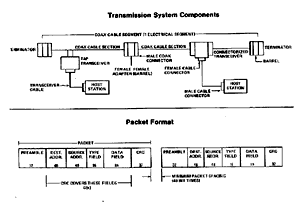
![]() Xerox, DEC
and Intel introduced the "Ethernet" standard for local networks. This
network standard made use of a coax cable to send messages / signals between
computers. Ethernet shall be quickly adopted by almost every network
manufacturer. Even Intel designed a special chip controller for this type of
network.
Xerox, DEC
and Intel introduced the "Ethernet" standard for local networks. This
network standard made use of a coax cable to send messages / signals between
computers. Ethernet shall be quickly adopted by almost every network
manufacturer. Even Intel designed a special chip controller for this type of
network.
![]() Hayes
Microcomputers Products announced the Micromodem 100 the first commercial modem.
It could transmit at 110 to 300 bps.
Hayes
Microcomputers Products announced the Micromodem 100 the first commercial modem.
It could transmit at 110 to 300 bps.
![]() CompuServe
and The Source on-line services open.
CompuServe
and The Source on-line services open.
![]() The first Computerized
Bulletin Board System (CBBS) opened to the public in Chicago.
The first Computerized
Bulletin Board System (CBBS) opened to the public in Chicago.
![]() Three
students on two universities of North Carolina (USA) used the Unix
to UNIX Copy Program (uucp) to put messages in a newsgroup. Usenet was born.
By 1991 Usenet hosts more than 35,000 nodes. (25)
Three
students on two universities of North Carolina (USA) used the Unix
to UNIX Copy Program (uucp) to put messages in a newsgroup. Usenet was born.
By 1991 Usenet hosts more than 35,000 nodes. (25)
![]() Magic Wand,
a word processor program became a competitor for Word Star. (25)
Magic Wand,
a word processor program became a competitor for Word Star. (25)
![]() Wayne Ratliff
developed the Vulcan database program based on the concept of JPLDIS, a database
program that ran on JPL computers. The marketing did not bring the results expected
and after a deal with George Tate (from Ashton-Tate) it was renamed into dBase
II. (2) There was no dBase I but both thought it better to
skip a nomination for marketing reasons. The Ashton-Tate company blew new life
in the marketing effort and the program became a huge succes. Mainly because
the interfacing was so easy to understand and open ended. In its final version
dBase II allowed up to 65,000 records, and up to 32 fields of 1Kb each. (25)
Wayne Ratliff
developed the Vulcan database program based on the concept of JPLDIS, a database
program that ran on JPL computers. The marketing did not bring the results expected
and after a deal with George Tate (from Ashton-Tate) it was renamed into dBase
II. (2) There was no dBase I but both thought it better to
skip a nomination for marketing reasons. The Ashton-Tate company blew new life
in the marketing effort and the program became a huge succes. Mainly because
the interfacing was so easy to understand and open ended. In its final version
dBase II allowed up to 65,000 records, and up to 32 fields of 1Kb each. (25)
![]() Texas Inst.
released the first 16-bit processor on the market: 9900
Texas Inst.
released the first 16-bit processor on the market: 9900
![]() Ada language
was developed by US Department of Defense; a highly structured, modular language
based on Pascal. Easy to learn, very readable but not very efficient. (25)
Ada language
was developed by US Department of Defense; a highly structured, modular language
based on Pascal. Easy to learn, very readable but not very efficient. (25)
![]() The first Atari
microcomputers Atari 400 and 800 came on the market. They offered 8 Kb RAM (expandable
to 48 Kb), a full Keyboard and a Sound and Graphics chips that were designed
by Joy Miner.
The first Atari
microcomputers Atari 400 and 800 came on the market. They offered 8 Kb RAM (expandable
to 48 Kb), a full Keyboard and a Sound and Graphics chips that were designed
by Joy Miner.
![]()
| Last Updated on February 5, 2004 | For suggestions please mail the editors |
Footnotes & References